Date: 12/20
/================================================/
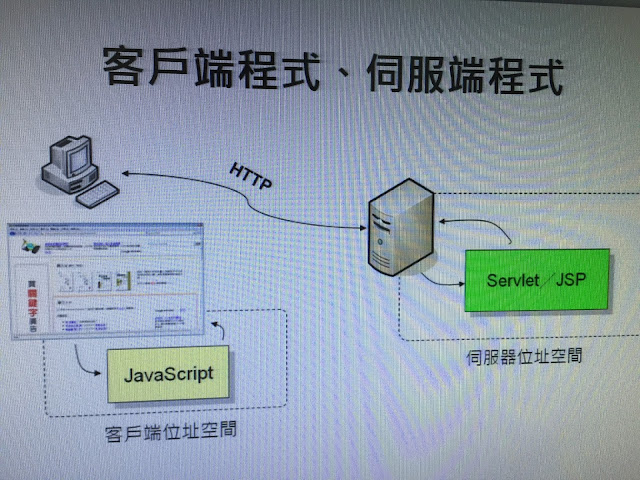
DAO(Data Access Object)資料存取物件
主要的功能是資料操作,屬於資料層的操作
client → JSP/Servlet → BO → DAO → Database
客戶層 顯示層 業務層 資料層 資源層
client → B/S開發架構,大都以Browser進行存取
顯示層 → 以JSP/Servlet進行頁面效果的顯示
Business Object→ 將多個最小的DAO進行組合變成一個業務邏輯--> BO
DAO→ 提拱多個最小性的DAO操作,例如新增刪除、修改
/================================================/
DAO → 由以下幾個部分組成:
Database Connection → 負責資料庫的開啟與關閉 (xxx.dbc.DatabaseConnection)
VO → 主要是屬性,setter、getter方法組成,與欄位相對應,每一個VO的組成都對應到一條記錄 (like JavaBean)
DAO → 定義操作的介面,新增、刪除、修改、按ID查詢等 (xxx.dao.ImplDAO)
Impl → DAO介面的真實實歸類別,完成實際的資料庫操作不負責開啟和關閉(xxx.dao.xxxImplDAO)
Proxy → 代理實現類別,完成資料庫的開啟和關閉 (xxx.dao.xxxDAOProxy)
Factory → 工廠類別,透過他取得一個DAO產生的實體物件 (xxx.factor.DAOFactory)
/================================================/
組成: 註冊系統 --> 將資料存到架設好的mySQL建表
1. index.jsp、emp_list.jsp、insert_success.jsp
2. com.demo => DatabaseConnection.java、Emp.java、IEmpDAO.java、IEmpDAOImpl.java、EmpDAOProxy.java、DAOFactory.java
3. com.dome.dbc => DatabaseConnection.java、MySQLDatabaseConnection.java
lifelong learning and ongoing creation
2015年12月21日 星期一
2015年12月17日 星期四
JAVA SL-314_12/13
JAVA SL-314_12/13
Date: 12/13
/======================================================/
<jsp:useBean>
與 import 功能相同
<jsp:useBean id=”產生的實體物件” scope="儲存範圍" class=”套件.class name” />
※ scope => 表示這個物件的儲存範圍,一共有四個屬性: page, request, session, application
/======================================================/
<jsp: setProerty>
可以透過 * 的形式完成屬性的自動設定
一其有4種方法
自動比對: <jsp: setProperty name=”實體的名稱(id)” property=”*” />
指定屬性: <jsp: setProperty name=”實體的名稱(id)” property=”屬性明稱” />
指定參數: <jsp: setProperty name=”實體的名稱(id)” property=”屬性明稱” param=”參數名稱” />
指定內容: <jsp: setProperty name=”實體的名稱(id)” property=”屬性明稱” value=”內容” />
/======================================================/
Date: 12/13
/======================================================/
<jsp:useBean>
與 import 功能相同
<jsp:useBean id=”產生的實體物件” scope="儲存範圍" class=”套件.class name” />
※ scope => 表示這個物件的儲存範圍,一共有四個屬性: page, request, session, application
/======================================================/
<jsp: setProerty>
可以透過 * 的形式完成屬性的自動設定
一其有4種方法
自動比對: <jsp: setProperty name=”實體的名稱(id)” property=”*” />
指定屬性: <jsp: setProperty name=”實體的名稱(id)” property=”屬性明稱” />
指定參數: <jsp: setProperty name=”實體的名稱(id)” property=”屬性明稱” param=”參數名稱” />
指定內容: <jsp: setProperty name=”實體的名稱(id)” property=”屬性明稱” value=”內容” />
/======================================================/
2015年12月6日 星期日
JAVA SL-314_12/06
Date: 12/06
/========================================================/
session物件
session的用處就是完成使用者的login logout
等常見功能,每一個session都表示不同的存取
使用者,其為javax.servlet.http.HttpSesion介面
所產生的實體物件
HttpSession介面中存在以下4種屬性操作方法:
1. 設定屬性 public void patValue(String name, Object value)
2. 取得屬性 public Object getValue(String name)
3. 刪除屬性 public void removeValue(String name)
4. 取得全部性屬性名稱 public String[ ] getValueNames()
/========================================================/
※ 作業系統伺服器+web伺服器(mysql+tomcat)
web伺服器是用來解譯web程式語言
※ JSP是一個很嚴謹的程式語言,因此相對的比較不容易被駭客入侵。
/========================================================/
/========================================================/
session物件
session的用處就是完成使用者的login logout
等常見功能,每一個session都表示不同的存取
使用者,其為javax.servlet.http.HttpSesion介面
所產生的實體物件
HttpSession介面中存在以下4種屬性操作方法:
1. 設定屬性 public void patValue(String name, Object value)
2. 取得屬性 public Object getValue(String name)
3. 刪除屬性 public void removeValue(String name)
4. 取得全部性屬性名稱 public String[ ] getValueNames()
/========================================================/
※ 作業系統伺服器+web伺服器(mysql+tomcat)
web伺服器是用來解譯web程式語言
※ JSP是一個很嚴謹的程式語言,因此相對的比較不容易被駭客入侵。
/========================================================/
2015年11月29日 星期日
JAVA SL-314_11/29
Date: 11/29
在JSP中為了簡化使用者開發JSP內建
9種物件供開發者使用
pageContext 頁面內容容器
request 請求者資訊
response 用戶端回應資料
session 儲存使用者資訊
application 使用者共同資訊
config 初始化參數伺服器設定
out 輸出
page
exception
page → 跳躍無效,一個頁面
request → 一次請求,跳躍然有效
session → 一次階段範圍中儲存 新開browser無效
application →整個 伺服器上儲存 all user使用
/===============================================/
在JSP中為了簡化使用者開發JSP內建
9種物件供開發者使用
pageContext 頁面內容容器
request 請求者資訊
response 用戶端回應資料
session 儲存使用者資訊
application 使用者共同資訊
config 初始化參數伺服器設定
out 輸出
page
exception
page → 跳躍無效,一個頁面
request → 一次請求,跳躍然有效
session → 一次階段範圍中儲存 新開browser無效
application →整個 伺服器上儲存 all user使用
/===============================================/
2015年11月23日 星期一
JAVA SL-314_11/22
JAVA SL-314
Date: 11/22
/*
<%!
public static final String INFO="www.google.com";
int x=0;
%>
<%
out.println("<h2>x="+x+++"</h2>"); //敘述
%>
<%!
public int add(int x, int y){
return x+y;
}
%>
<%!
class Person {
private String name;
private int age;
Person(String name, int age){
this.name=name;
this.age=age;
}
public String toString(){
return "name="+this.name+"; age="+this.age;
}
}
%>
<%!
out.println("<h3>INFO"+INFO+"</h3>");
out.println("<h3>3+5="+add(3,5)+"</h3>");
out.println("<h3>"+new Person("name",18)+"</h3>");
%>
*/
/====================================================/
想要在自己的 NB 上架 Drupal 及 Wordpress 等 Open Source 免費架站軟體的開發測試
環境,以前都是從 Apache 、PHP 、 MySQL 、phpMyAdmin 一個一個的安裝設定,
還蠻麻煩的,而且也容易出問題,現在直接用 AppServ 四合一包還蠻方便,安裝快速
又容易,很快就可以準備好自己的開發測試環境了 !
1. 先下載appserv-win32-2.5.10.exe:
https://drive.google.com/file/d/0B8Dfp4n5Q35CVjY0SjV3QmljTDQ/view?usp=sharing
2. 執行安裝 ---> 以系統管理員執行
appserv-win32-2.5.10.exe
3. 點按next
4. 點按I agree
5. 依照下列指示安裝下一步
6. 安裝完成後,可以查看工作管理員--->服務--->Apache2.2、mysql
7. 服務都起來後,執行google輸入localhost,就會看見以下畫面,再點選指示
8. 輸入root,及密碼
9. AppServ 2.5.10 安裝測試成功
/====================================================/
Page指令
1. contemt Type ---> 定義JSP字元的編號和頁面MIME的回應型態。
2. import ---> 要載入那些套件。
3. pageEncoding ---> JSP頁面的字元編碼。
3. info ---> 資訊。
4. language ---> 指令碼語言。
5. is ErrorPage ---> 此頁面是否為出錯的處裡頁true處理,false則無法處理。
/====================================================/
include指令 => @
可分為動態包含及靜態包含:
1. 靜態包含---> 就是包含一個文字或JSP檔案,過程是靜態的,
例如: JSP檔案、html檔案、文字檔。
2. 動態包含---> 是使用<jsp: include>可以將靜態及動態頁面一
起包含進來,分別處裡,先處理靜態頁面結果。
ex:
<h3>靜態包含操作</h3>
<%@ include file = "info.html"% >
<%@ include file = "info.inc"%>
※page,include => %後都要加@
/====================================================/
receive_param.jsp
/*
<html>
<head>
</head>
<body>
<h1>參數一:
<%= request.getParameter("name") %></h1>
<h2>參數二:
<%= request.getParameter("info") %></h2>
</body>
</html>
Date: 11/22
/*
<%!
public static final String INFO="www.google.com";
int x=0;
%>
<%
out.println("<h2>x="+x+++"</h2>"); //敘述
%>
<%!
public int add(int x, int y){
return x+y;
}
%>
<%!
class Person {
private String name;
private int age;
Person(String name, int age){
this.name=name;
this.age=age;
}
public String toString(){
return "name="+this.name+"; age="+this.age;
}
}
%>
<%!
out.println("<h3>INFO"+INFO+"</h3>");
out.println("<h3>3+5="+add(3,5)+"</h3>");
out.println("<h3>"+new Person("name",18)+"</h3>");
%>
*/
/====================================================/
想要在自己的 NB 上架 Drupal 及 Wordpress 等 Open Source 免費架站軟體的開發測試
環境,以前都是從 Apache 、PHP 、 MySQL 、phpMyAdmin 一個一個的安裝設定,
還蠻麻煩的,而且也容易出問題,現在直接用 AppServ 四合一包還蠻方便,安裝快速
又容易,很快就可以準備好自己的開發測試環境了 !
1. 先下載appserv-win32-2.5.10.exe:
https://drive.google.com/file/d/0B8Dfp4n5Q35CVjY0SjV3QmljTDQ/view?usp=sharing
2. 執行安裝 ---> 以系統管理員執行
appserv-win32-2.5.10.exe
3. 點按next
6. 安裝完成後,可以查看工作管理員--->服務--->Apache2.2、mysql
7. 服務都起來後,執行google輸入localhost,就會看見以下畫面,再點選指示
/====================================================/
Page指令
1. contemt Type ---> 定義JSP字元的編號和頁面MIME的回應型態。
2. import ---> 要載入那些套件。
3. pageEncoding ---> JSP頁面的字元編碼。
3. info ---> 資訊。
4. language ---> 指令碼語言。
5. is ErrorPage ---> 此頁面是否為出錯的處裡頁true處理,false則無法處理。
/====================================================/
include指令 => @
可分為動態包含及靜態包含:
1. 靜態包含---> 就是包含一個文字或JSP檔案,過程是靜態的,
例如: JSP檔案、html檔案、文字檔。
2. 動態包含---> 是使用<jsp: include>可以將靜態及動態頁面一
起包含進來,分別處裡,先處理靜態頁面結果。
ex:
<h3>靜態包含操作</h3>
<%@ include file = "info.html"% >
<%@ include file = "info.inc"%>
※page,include => %後都要加@
/====================================================/
//include.jsp<br />
<%@ page language="java" import="java.util.*" pageEncoding="BIG5"%>
<!DOCTYPE HTML PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01 Transitional//EN">
<html>
<head>
</head>
<body>
<%
int x=10;
%>
<h1>include.jsp--x<%=x%></h1>
</body>
</html>
/====================================================/receive_param.jsp
/*
<html>
<head>
</head>
<body>
<h1>參數一:
<%= request.getParameter("name") %></h1>
<h2>參數二:
<%= request.getParameter("info") %></h2>
</body>
</html>
*/
/====================================================/
App2.jsp (動態)
/*
<html>
<head>
</head>
<body>
<h1>動態包含操作</h1>
<%
String name="Google";
%>
<jsp:include page="receive_param.jsp">
<jsp:param name="name" value="<%= name %>"/>
<jsp:param name="info" value="www.google.com"/>
</jsp:include>
<%
int x=100;//變數
%>
<h1>App2.jsp...x<%=x %></h1>
<jsp:include.page="include.jsp"/>
</body>
</html>
*/
/====================================================/
App2.jsp (靜態)
/*
<html>
<head>
</head>
<body>
<h1>靜態包含操作</h1>
<%
int x=100;//變數
%>
<h1>include.jsp...x</h1>
<include.page="include.jsp"/>
</body>
</html>
*/
/====================================================/
靜態 ---> 全部包含再處理。
動態 ---> 先處理,再把結果包含進去。
/====================================================/
跳轉指令語法
不傳遞參數
<jsp:forward page="要跳轉的檔案or運算式"/>
要傳遞參數
<jsp: forward page="要跳轉的檔案or運算式"/>
<jsp: param name="參數名稱" value="參數名稱" value="參數內容"/>
</jsp: forword>
/====================================================/
2015年11月15日 星期日
JAVA SL-314_11/15
JAVA SL-314
Date: 11/15
※ HTTP/FTP/HTTPS
基於請求/回應模型
沒有狀態的通訊協定
| HTTP| 請求URL| 請求的資源 | HTTP版本
http:// /download.do?file… /HTTP 1.1
---> 向伺服器取得指定的資源
1. 可以請求的參數有限 (依brower的版本而有不同)
2. 不適合大量的資料
※ POST
請求發佈(POST)資訊給伺服器
1. 大量的資料發送都會使用POST
2. 請求資訊移到主體,網址列不會出現請求參數
3. 一般即使請求資料不多也大都會採用POST
※GET(等冪) or POST(非等冪)
1. 過長的請求參數 ---> POST
2. 較敏感的參數資料 ---> POST
3. 希望可以讓使用者設定書籤,以便日後瀏覽 ---> GET
4. 考慮Browser會cache資料問題 ---> GET
※採用MVC架構來設計軟體系統會比較好維護,擴充及除錯。
web---> 實體server → http伺服器 → web容器 ---> servlert
Java → JVM
Servlert / JSP --->web容器 ----> my eclipse
php容器---> apahe
ASP.NET容器 ---> IIS
/========================================================/
註解
1. // 單行
2. /*...*/ 多行
3. <!--xoo-->
/========================================================/
Script
<% %>
定義區域變數,敘述
2. <%!%>
定義全域變數,方法,類別
3. <%=%>
定異常數或運算式
/========================================================/
/========================================================/
使用MyEclipse
版本: MyEclipse 8.5
接下來讓我來lab吧!
首先開啟MyEclipse,接著在WebRoot建立新的html
/========================================================/
再到google輸入 ---> http://aaronhuang:8080/DEMO/MyHtml.html
再輸入123
Date: 11/15
※ HTTP/FTP/HTTPS
基於請求/回應模型
沒有狀態的通訊協定
| HTTP| 請求URL| 請求的資源 | HTTP版本
http:// /download.do?file… /HTTP 1.1
---> 向伺服器取得指定的資源
1. 可以請求的參數有限 (依brower的版本而有不同)
2. 不適合大量的資料
※ POST
請求發佈(POST)資訊給伺服器
1. 大量的資料發送都會使用POST
2. 請求資訊移到主體,網址列不會出現請求參數
3. 一般即使請求資料不多也大都會採用POST
※GET(等冪) or POST(非等冪)
1. 過長的請求參數 ---> POST
2. 較敏感的參數資料 ---> POST
3. 希望可以讓使用者設定書籤,以便日後瀏覽 ---> GET
4. 考慮Browser會cache資料問題 ---> GET
※採用MVC架構來設計軟體系統會比較好維護,擴充及除錯。
web---> 實體server → http伺服器 → web容器 ---> servlert
Java → JVM
Servlert / JSP --->web容器 ----> my eclipse
php容器---> apahe
ASP.NET容器 ---> IIS
/========================================================/
註解
1. // 單行
2. /*...*/ 多行
3. <!--xoo-->
/========================================================/
Script
<% %>
定義區域變數,敘述
2. <%!%>
定義全域變數,方法,類別
3. <%=%>
定異常數或運算式
/========================================================/
使用MyEclipse
版本: MyEclipse 8.5
接下來讓我來lab吧!
首先開啟MyEclipse,接著在WebRoot建立新的html
//MyHtml.html
<html>
<head>
<title>HTML_Javascript</title>
<script language="javascript"><!--Javasript-->
function show(){ //定義函數
var show = document.myform.name.value; //取得輸入內容
alert("輸入的內容是:"+show);
}
</script>
</head>
<body>
<form action="" method="post" name="myform">
請輸入內容:<input name="name" type="text" />
<input onclick="show()" type="button" value="顯示" />
</form>
</body>
</html>
/========================================================/
再到google輸入 ---> http://aaronhuang:8080/DEMO/MyHtml.html
再輸入123
2015年10月19日 星期一
JAVA SL-275_10/18
JAVA SL-275_10/18
Date: 10/18
//============================================================//
常用的 Java 圖形 Lib (java 7.0 版以後,兩種可以混用):
AWT
Swing
一般功能表是由三種類別所建立:
MenuBar
Menu
MenuItem
java.lang.Object
java.awt.MenuComponent → java.awt.MenuBar
java.awt.MenuComponent → java.awt.MenuItem ─ java.awt.Menu
設計的參數及概念:
監聽事件 (event listener) 架構圖:
//============================================================//
Date: 10/18
//============================================================//
常用的 Java 圖形 Lib (java 7.0 版以後,兩種可以混用):
AWT
Swing
一般功能表是由三種類別所建立:
MenuBar
Menu
MenuItem
java.lang.Object
java.awt.MenuComponent → java.awt.MenuBar
java.awt.MenuComponent → java.awt.MenuItem ─ java.awt.Menu
設計的參數及概念:
監聽事件 (event listener) 架構圖:
//============================================================//
//app_1.java
import java.awt.*;
import java.awt.event.*;
public class app_1 extends Frame implements ActionListener{
static app_1 frm=new app_1();
static Button btn1=new Button("Yellow");
static Button btn2=new Button("Green");
static Button btn3=new Button("Exit");
public static void main(String args[]){
btn1.addActionListener(frm);
btn2.addActionListener(frm);
btn3.addActionListener(frm);
frm.setTitle("ActionEvent");
frm.setLayout(new FlowLayout(FlowLayout.CENTER));
frm.setSize(300,200);
frm.add(btn1);
frm.add(btn2);
frm.add(btn3);
frm.setVisible(true); //一定要show出,不然無法顯示。
frm.addWindowListener(new WindowAdapter(){ //視窗右上角x功能
public void windowClosing(WindowEvent e){
System.exit(0);
}
});
}
public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent e){
Button btn=(Button)e.getSource();//取得事件來源物件。
if(btn==btn1)
frm.setBackground(Color.YELLOW);
if(btn==btn2)
frm.setBackground(Color.GREEN);
if(btn==btn3)
System.exit(0);
}
}
//============================================================////app_2.java
import java.awt.Checkbox;
import java.awt.CheckboxGroup;
import java.awt.*;
import java.awt.event.*;
public class app_2 extends Frame implements ItemListener{
static app_2 frm=new app_2();
static Checkbox ckb1=new Checkbox("Java");
static Checkbox ckb2=new Checkbox("PHP");
static Label lab=new Label("Select one");
public static void main(String args[]){
CheckboxGroup grp=new CheckboxGroup();
frm.setSize(300,200);
frm.setTitle("app_2 Programmer");
frm.setLayout(new FlowLayout(FlowLayout.CENTER));
ckb1.setCheckboxGroup(grp);
ckb2.setCheckboxGroup(grp);
lab.setBackground(Color.orange);
ckb1.addItemListener((ItemListener) frm);
ckb2.addItemListener((ItemListener) frm);
frm.add(ckb1);
frm.add(ckb2);
frm.add(lab);
frm.setVisible(true);
frm.addWindowListener(new WindowAdapter(){ //視窗右上角x功能
public void windowClosing(WindowEvent e){
System.exit(0);
}
});
}
@Override
public void itemStateChanged(ItemEvent e) {
if(ckb1.getState()==true)
lab.setText("Java");
else if(ckb2.getState()==true)
lab.setText("PHP");
}
}
//============================================================////app3.java
import java.awt.*;
import java.awt.event.*;
public class app3 extends Frame implements ActionListener{
static app3 frm=new app3();
static Label lab=new Label("Hellow JAVA",Label.CENTER);
static MenuBar mb=new MenuBar();
static Menu menu1=new Menu("Style");
static Menu menu2=new Menu("Exit");
static MenuItem mi1=new MenuItem("plane");
static MenuItem mi2=new MenuItem("bold");
static MenuItem mi3=new MenuItem("italic");
static MenuItem mi4=new MenuItem("close window");
//Dialog --> 要呼叫 show() method 才可以顯示
static Button close_btn=new Button("Close");
static Button cancel_btn=new Button("Cancel");
static Dialog dlg=new Dialog(frm);
static WinLis wlis=new WinLis();
public static void main(String args[]){
mb.add(menu1);
mb.add(menu2);
menu1.add(mi1);
menu1.add(mi2);
menu1.add(mi3);
menu2.add(mi4);
mi1.addActionListener(frm);
mi2.addActionListener(frm);
mi3.addActionListener(frm);
mi4.addActionListener(frm);
lab.setFont(new Font("Dialog",Font.PLAIN,24));
frm.add(lab);
frm.setSize(280,150);
frm.setTitle("app_3 Programmer");
frm.setMenuBar(mb);
frm.setVisible(true);
dlg.setTitle("Are you sure?");
dlg.setSize(140,100);
dlg.setLayout(new FlowLayout(FlowLayout.CENTER,5,30));
dlg.add(close_btn);
dlg.add(cancel_btn);
close_btn.addActionListener(frm);
cancel_btn.addActionListener(frm);
frm.addWindowListener(wlis);
/*frm.addWindowListener(new WindowAdapter(){ //視窗右上角x功能
public void windowClosing(WindowEvent e){
System.exit(0);
}
});*/
}
static class WinLis extends WindowAdapter{
public void windowClosing(WindowEvent e){
dlg.setLocation(80, 30);
dlg.show();
}
}
@Override
public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent e) {
//MenuItem mi=(MenuItem)e.getSource();
if(e.getSource()==mi1)
lab.setFont(new Font("Dialog",Font.PLAIN,30));
else if(e.getSource()==mi2)
lab.setFont(new Font("Dialog",Font.BOLD,30));
else if(e.getSource()==mi3)
lab.setFont(new Font("Dialog",Font.ITALIC,30));
else if(e.getSource()==mi4)
frm.dispose();//關閉式窗
//Button btn=(Button)e.getSource();
else if(e.getSource()==close_btn){
dlg.dispose();
frm.dispose();
}
else if(e.getSource()==cancel_btn){
dlg.hide(); //隱藏
}
}
}
//============================================================//
2015年10月5日 星期一
JAVA SL-275_10/04
JAVA SL-275_10/04
Date: 10/04
List
作用是收集物件,並以索引益式保留收集的物件順序。
ArrayList
在陣列中的排序使用可以得到較快的速度,
如果是需要調整索引順序時,則會有較差的表現。
LinkedList
在實作 List 介面時,採用了 (Link) 結構。
first > Object > Object > Object
next next next
Node Node Node
如果要指定索引隨機存取物件時,不建議用 LinkedList,其每次存取都會從頭 (first ) 開始,
但若只是調整索引順序,從還是可以使用 LinkedList。
//================================================================//
支援佇列操作的 Queue
繼承自 Collection,所以它也具有 Collection 的 add(), remove(), element() 等方法。
一操作失敗時,會拋出例外
Queue 定義了自己的 offer(), poll(), pee,() 等方法。
一操作失敗時會傳回特定值
offer() 用來在佇列後端加入物件
成功→True, 失敗→false
poll() 取出佇列前端物件,若佇列為空則傳回 null.
peek() 取得(但不取出)佇列前端物件,若佇列為空則傳回 null.
//================================================================//
想對佇列的前端與尾端進行操作,在前端加入物件與取出物件,在尾端加入與取出物件, Queue 的子介面 Deque 就定義了這類行為。
addFirst(), removeFirst(), getFirst().
addLast(), removeLast(), getLast().
操作失敗時會傳回例外
offerFirst(), pollFirst(), peekFirst().
offerLast(), pollLast(), peekLast().
操作物敗時會傳回特定值
//================================================================//
排序收集的物件
java.util.Collection 提供有 sort() 方法,由於必須有索引才能進行排序,
因此 Collection 的 sort() 方法接受 List 實作的物件。
//================================================================//
//================================================================//
Date: 10/04
List
作用是收集物件,並以索引益式保留收集的物件順序。
ArrayList
在陣列中的排序使用可以得到較快的速度,
如果是需要調整索引順序時,則會有較差的表現。
LinkedList
在實作 List 介面時,採用了 (Link) 結構。
first > Object > Object > Object
next next next
Node Node Node
如果要指定索引隨機存取物件時,不建議用 LinkedList,其每次存取都會從頭 (first ) 開始,
但若只是調整索引順序,從還是可以使用 LinkedList。
//================================================================//
支援佇列操作的 Queue
繼承自 Collection,所以它也具有 Collection 的 add(), remove(), element() 等方法。
一操作失敗時,會拋出例外
Queue 定義了自己的 offer(), poll(), pee,() 等方法。
一操作失敗時會傳回特定值
offer() 用來在佇列後端加入物件
成功→True, 失敗→false
poll() 取出佇列前端物件,若佇列為空則傳回 null.
peek() 取得(但不取出)佇列前端物件,若佇列為空則傳回 null.
//================================================================//
想對佇列的前端與尾端進行操作,在前端加入物件與取出物件,在尾端加入與取出物件, Queue 的子介面 Deque 就定義了這類行為。
addFirst(), removeFirst(), getFirst().
addLast(), removeLast(), getLast().
操作失敗時會傳回例外
offerFirst(), pollFirst(), peekFirst().
offerLast(), pollLast(), peekLast().
操作物敗時會傳回特定值
//================================================================//
排序收集的物件
java.util.Collection 提供有 sort() 方法,由於必須有索引才能進行排序,
因此 Collection 的 sort() 方法接受 List 實作的物件。
//================================================================//
//================================================================//
//MapDemo.java
import java.util.*;
public class MapDemo {
public static void main(String args[]){
HashMap t = new HashMap();
t.put("A", "SCJP");
t.put(new Integer(100),new Integer(200));
t.put(new Object(),"SCBCD");
t.put(null, null);
System.out.println(t.toString());
System.out.println("keyA:"+t.get("A"));
System.out.println("keyB:"+t.get("B"));
}
}
//================================================================////取間值
import java.util.*;
import java.util.Map.Entry;
public class MapkeyValue {
public static void main(String args[]){
Map<String,String> map = new TreeMap<>();
map.put("one","一");
map.put("two","二");
map.put("three","三");
foreach(map.entrySet());
}
private static void foreach(Iterable<Map.Entry<String,String>>iterable){
for(Map.Entry<String, String> entry:iterable){
System.out.printf("鑑%s 值%s %n", entry.getKey(), entry.getValue());
}
}
}
//================================================================////Message.java
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.Scanner;
import java.util.*;
public class Messages {
public static void main(String args[]){
Map<String,String> messages = new HashMap<>();
messages.put("Justin","Hello Justin的訊息");
messages.put("Monic","給Monic的禮物");
messages.put("Irene","Irene的喵喵叫");
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.print("取得誰的訊息");
String str = messages.get(scanner.nextLine());
System.out.println(str);
System.out.println(messages);
}
}
//================================================================////NewClass.java
import java.util.*;
public class NewClass {
public static void main(String args[]){
Queue q = new LinkedList();
q.offer("First");
q.offer("Second");
q.offer("Third");
Object o;
System.out.println(q.toString());
/* while((o = q.poll()) != null){
String s = (String)o;
System.out.print(s+" ");
}*/
while((o = q.peek()) != null){ //跑無窮迴圈
String s = (String)o;
System.out.print(s+" ");
q.remove();
}
System.out.println(q.toString());
}
}
//================================================================////QueueDemo.java
import java.util.*;
public class QueueDemo {
public static void main(String args[]){
Queue<String> q = new LinkedList<String>();
q.offer("SCJP");
q.offer("SCWCD");
q.offer("SCBCD");
System.out.println(q.toString()+" ");
Iterator a = q.iterator();
while(a.hasNext()){
String s = (String)a.next();
System.out.print(s+" ");
}
}
}
//================================================================////RequestQueue.java
import java.util.*;
interface Request{
void execute();
}
public class RequestQueue {
public static void main(String args[]){
Queue requests = new LinkedList();
//模擬請求加入佇列
for(int i=1;i<6 execute="" i="" math.random="" n="" new="" null="" pre="" private="" process="" public="" request.execute="" request="(Request)requests.poll();" requests.offer="" requests.peek="" requests="" s="" static="" system.out.printf="" ueue="" void="" while="">
//================================================================//
練習:
Link.java、LinkDemo.java、SimpleLinkedList.java
//Link.java.java
class Link{
private class Node{
Object o;
Node next;
Node(Object o){
this.o=o;
}
}
private Node first;
public void add(Object o){
Node last;
if(first==null){
first=new Node(o);
}
else{
last=first;
while(last.next!=null){
last=last.next;
}
last.next=new Node(o);
}
}
public Object get(int index){
int size=size();
if(index>=size){
throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException(String.format("Index:%d, size:%d",index,size));
}
int count=0;
Node last=first;
while(count<index){
last=last.next;
count++;
}
return last.o;
}
public int size(){
if(first==null)
return 0;
Node last=first;
int count=1;
while(last.next!=null){
last=last.next;
count++;
}
return count;
}
}
//LinkDemo.java
public class LinkDemo {
public static void main(String args[]){
Link l = new Link();
String s0 = "hello-0";
String s1 = "hello-1";
String s2 = "hello-2";
String s3 = "hello-3";
l.add(s0);
l.add(s1);
l.add(s2);
l.add(s3);
System.out.println(l.size());
System.out.println((String)l.get(3));
System.out.println((String)l.get(0));
}
}
//SimpleLinkedList.java
public class SimpleLinkedList {
private class Node{
//將收集的物件用/vode封裝
Node(Object o){
this.o=o;
}
Object o;
Node next;
}
private Node first; //第一個節點
public void add(Object o){ //新增一個Node封裝物件,並由上一個o Node物件參考
if(first == null){
first=new Node(o);
}
else{
Node last = first;
while(last.next != null){
last=last.next;
}
last.next=new Node(o);
}
}
public int size(){ //走訪所有Node計數並取得長度
int count=0;
Node last=first;
while(last.next != null){
last=last.next;
count++;
}
return count;
}
public Object get(int index){ //走訪所有Node計數並取得對應索引順序
int size=size();
if(index > size){
throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException(
String.format("Index: %d,Size: %d", index, size));
}
int count=0;
Node last=first;
while(count < index){
last=last.next;
count++;
}
return last.o;
}
}
//================================================================//
import java.util.*;
class Account implements Comparable{
private String name;
private String number;
private int balance;
Account(String name,String number,int balance){
this.name=name;
this.number=number;
this.balance=balance;
}
public String toString(){
return String.format("Account(%s %s %d)",name,number,balance);
}
public int comparTo(Object o){
Account other=(Account)o;
return this.balance-other.balance;
}
@Override
public int compareTo(Object o) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
return 0;
}
}
public class Sort2 {
public static void main(String arg[]){
List accounts=Arrays.asList(
new Account("Justin","x1234",1000),
new Account("Monic","x5678",500),
new Account("Irene","x2345",100)
);
Collections.sort(accounts);
System.out.println(accounts);
}
}
//================================================================//
//Stack.java
import java.util.*;
public class Stack {
private Deque deque = new ArrayDeque();
private int capacity;
public Stack(int capacity){
this.capacity=capacity;
}
public boolean push (Object o){
if(deque.size()+1 > capacity){
return false;
}
return deque.offerLast(o);
}
public Object pop( ){
return deque.pollLast();
}
public Object peek(){
return deque.peekLast();
}
public int size(){
return deque.size();
}
public static void main(String args[]){
Stack stack = new Stack(4);
stack.push("Justin");
stack.push("Lisa");
stack.push("John");
System.out.println(stack.pop());
System.out.println(stack.peek());
System.out.println(stack.size());
}
}
//================================================================//
2015年10月4日 星期日
程式語言那麼多,為什麼 Google 偏愛 JS?
程式語言那麼多,為什麼 Google 偏愛 JS?
轉貼自:http://buzzorange.com/techorange/2015/09/29/google-javascript/
2015年10月3日 星期六
2015年9月20日 星期日
JAVA SL-275_09/20
/*
join
如果 A 執行緒正在運行,流程中允許 B 執行緒加入,等到 B 執行緒執行完畢再繼續 A 執行緒流程就可以使用 join() 方法完成需求,當執行緒使用 join() 加入至另一執行緒時,另一執行緒會等待被加入的執行緒工作完畢然後再續繼它的動作。
*/
//*****************************************************************************
join
如果 A 執行緒正在運行,流程中允許 B 執行緒加入,等到 B 執行緒執行完畢再繼續 A 執行緒流程就可以使用 join() 方法完成需求,當執行緒使用 join() 加入至另一執行緒時,另一執行緒會等待被加入的執行緒工作完畢然後再續繼它的動作。
*/
//*****************************************************************************
//joinDemo.java
public class joinDemo{
public static void main(String args[]){
System.out.println("Main thread 開始…");
Thread threadB = new Thread(){
public void run(){
try{
System.out.println("Thread B 開始…");
for(int i=0;i<5 ain="" b="" catch="" e.printstacktrace="" e="" ex.printstacktrace="" ex="" hread="" i="" main="" nterruptedexception="" pre="" s="" system.out.println="" thread.sleep="" thread="" threadb.join="" threadb.start="" try="">
//*****************************************************************************
/*
Thread Group
每個執行緒都屬於某個執行緒群組,可以使用以下程式片段取得目前執行緒所屬的執行緒群組。
Thread.currentThread().getThreadGroup().getName();
可以自行指定執行緒群組,執行緒一旦加入,即無法更改群組。
java.lang.ThreadGroup 可以管理群組中的執行緒。
*/
//*****************************************************************************
//ThreadGroupDemo.java
public class ThreadGroupDemo {
public static void main(String args[]){
ThreadGroup tg1 = new ThreadGroup("tg1");
Thread t1 = new Thread(tg1, new Runnable(){
public void run(){
throw new RuntimeException("t1 測試例外");
}
},"tg1");
t1.setUncaughtExceptionHandler(new Thread.UncaughtExceptionHandler() {
public void uncaughtException(Thread t, Throwable e) {
System.out.printf("%s ... %s%n", t.getName(), e.getMessage());
}
});
Thread t2 = new Thread(tg1, new Runnable(){
public void run(){
throw new RuntimeException("t2 測試例外");
}
},"tg2");
t1.start();
t2.start();
}
}
//*****************************************************************************
// 兩執行緒同時間點別相同的方法,會出現競速狀態出現 Error
// 下例的 Error: Exception in thread "Thread-0" java.lang.ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException
// java.lang.OutOfMemoryError 先不管它,此處為了探討競速物件。
import java.util.Arrays;
public class ArrayList {
private Object[] list;
private int next;
public ArrayList(int capacity){
list = new Object[capacity];
}
public ArrayList(){
this(16);
}
public void add(Object o){
//System.out.println("add start...");
if(next == list.length){
list = Arrays.copyOf(list, list.length * 2);
}
list[next++]=o;
}
public Object get(int index){
return list[index];
}
public int size(){
return next;
}
public static void main(String args[]){
ArrayList list = new ArrayList();
Thread t1 = new Thread(){
public void run(){
while(true){
list.add(1);
}
}
};
Thread t2 = new Thread(){
public void run(){
while(true){
list.add(2);
}
}
};
t1.start();
t2.start();
}
}
//-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
// 同上範例,加入 synchronized 除掉競速問題
// 同樣會有 java.lang.OutOfMemoryError 此處不管它
import java.util.Arrays;
public class ArrayList {
private Object[] list;
private int next;
public ArrayList(int capacity){
list = new Object[capacity];
}
public ArrayList(){
this(16);
}
synchronized public void add(Object o){
if(next == list.length){
list = Arrays.copyOf(list, list.length * 2);
}
list[next++]=o;
}
public Object get(int index){
return list[index];
}
public int size(){
return next;
}
public static void main(String args[]){
ArrayList list = new ArrayList();
Thread t1 = new Thread(){
public void run(){
while(true){
synchronized(list){
list.add(1);
System.out.println(list.get(list.size()-1));
}
}
}
};
Thread t2 = new Thread(){
public void run(){
while(true){
synchronized(list){
System.out.println(list.get(list.size()-1));
list.add(2);
}
}
}
};
t1.start();
t2.start();
}
}
//*****************************************************************************
/*
synchronized 與 volatile
在 Java 中對資可見性的要求,可以使用 volatile 達到,在變數上宣告,表示變數是不穩定的是易變的,也就是可能在多執行緒下存取,可保證變數的可見性,也是是若執行緒變動了變數值,另一執行緒一可以看到變更。
不允許執行緒快取,變數的存取是在共享記憶體中進行。
*/
//*****************************************************************************
// 寫一個練習,分為四個檔案:
// Producer.java
package java_0920;
public class Producer implements Runnable {
private Clerk clerk;
public Producer(Clerk clerk){
this.clerk = clerk;
}
public void run(){
System.out.println("生產者開始生產…");
for(int product=1;product<=10;product++){
try{
Thread.sleep((int)(Math.random()*3000));
}catch(InterruptedException ex){
throw new RuntimeException(ex);
}
clerk.setProduct(product);
}
}
}
//Consumer.java
package java_0920;
public class Consumer implements Runnable {
private Clerk clerk;
public Consumer(Clerk clerk){
this.clerk = clerk;
}
public void run(){
System.out.println("消費者開始消費…");
for(int i=1;i<=10;i++){
try{
Thread.sleep((int)(Math.random()*3000));
}catch(InterruptedException ex){
throw new RuntimeException(ex);
}
int product = clerk.getProduct();
}
}
}
//Clerk.java
package java_0920;
public class Clerk {
private int product = -1 ;
public synchronized int getProduct() {
while(this.product != -1){
try{
wait();
}catch(InterruptedException e){
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
int p = this.product;
System.out.printf("消費者取得…(%d)%n",this.product);
this.product=-1;
notify();
return p;
}
public synchronized void setProduct(int product) {
while(this.product != -1){
try{
wait();
}catch(InterruptedException e){
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
this.product = product;
System.out.printf("生產者設定…(%d)%n", this.product);
notify();
}
}
//ProducerConsumerDemo.java
package java_0920;
public class ProducerConsumerDemo {
public static void main(String args[]){
Clerk clerk = new Clerk();
new Thread(new Producer(clerk)).start();
new Thread(new Consumer(clerk)).start();
}
}
//*****************************************************************************
/*
Collection 集合架構介面關係圖
※可動態產生集合元素
可置入不同型別的資料,依照各集合的特性有:排序性、順序性、不允許重複、是否有鍵值的使用。
<String, Integer> 泛型
public interface Set implements Collection
其特性是無順序性,並且元素與元素之間不得重複。
其利用 equal() 方法來判斷加入的物件是否重複,Set 是資料具唯一性但無順序性的集。
※ 不是用 equals (用於比較字串)
*/
//*****************************************************************************
//HashSet
//沒有順序性 (擺放位置是根據 hashCode) 不允許重複
import java.util.*;
public class HashSetDemo {
public static void main(String argsp[]){
HashSet<String> s = new HashSet<String>();
s.add("SCJP");
s.add("SCWCD");
s.add("SCBCD");
Iterator i = s.iterator();
while(i.hasNext()){
String str = (String)i.next();
System.out.println(str + " ");
}
}
}
//*****************************************************************************
//練習:重複輸入的資料只顯示一個
import java.util.*;
public class HashSetDemo2 {
public static void main(String args[]){
Set<String> words = new HashSet<String>();
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("Input english word:");
String line = scanner.nextLine();
String tokens[] = line.split(" ");
for(String token:tokens){
words.add(token);
}
System.out.printf("不重複的單字有(%d)個 %s%n", words.size(), words);
}
}
//執行後自己手動輸入單字,以空白隔開,會自動過濾並顯示出不重複單字。
//*****************************************************************************
import java.util.*;
class Student {
private String name;
private String number;
Student(String name, String number){
this.name=name;
this.number=number;
}
public String toString(){
return String.format("(%s %s)", name, number);
}
}
public class StudentDemo{
public static void main(String args[]){
/*
Set<String> set = new HashSet<String>();
set.add(new Student("Justin", "B6789").toString());
set.add(new Student("Monica", "B8765").toString());
set.add(new Student("Joe", "B213678").toString());
*/
Set set = new HashSet();
set.add(new Student("Monica", "B8765"));
set.add(new Student("Justin", "B6789"));
set.add(new Student("Joe", "B213678"));
System.out.println(set);
}
}
2015年9月13日 星期日
JAVA SL-275_09/13
/*
‧使用 finally
無論 try 區塊中有無發生例外,若撰寫有 finally 區塊,則 finally 區塊一定會執行,如果程式撰寫的流程中先 return 了,而且也有寫 finally 區塊,那 finally 區塊會先執行完後,再將值傳回。
try{
do something…
}catch{
do something…
}finally{ // Always 會執行,且優先過 try-cache
….
}
可以允許的程式寫法:
try-cache
try-finally
try-cache-finally
錯誤的寫法:
catch finally
*/
/****************************************************************************** /
/*
java.lang.AutoCloseable 介面
JDK 7 新增了自動關閉資源語法可用的套件,必須實作 java.lang.AutoCloseable 介面,其僅定義了 close() 方法。
package java.lang.*;
public interface AutoCloseable{
void close() throws Exception;
}
*/
/*
執行序流程圖
---
執行序的執行狀態:
起始狀態
Thread t = new Thread();
可執行狀態
Thread t = new Thread();
t.start(); t.yield();
執行狀態
實作 Runnable 介面
繼承 Thread 類別
public void run(){
……
}
非可執行狀態
Thread t - new Thread();
sleep().wait().suspend();
結束狀態
stop()
正常結束
*/
/******************************************************************************/
// 練習 Thread 寫龜兔賽跑
public class TortoisHareDemo{
public static void main(String args [])throws InterruptedException{
boolean flags[]={true,false};
int totalStep=10;
int tortoiseStep=0;
int hareStep=0;
System.out.println("龜兔賽跑開始…");
while(tortoiseStep < totalStep && hareStep <totalStep){
Thread.sleep(1000);
tortoiseStep++;
System.out.printf("烏龜跑了 %d 步…%n", tortoiseStep);
boolean isHareSleep=flags[((int)(Math.random()*10))%2];
if(isHareSleep){
System.out.println("兔子睡著了…zzz");
}else{
hareStep+=2;
System.out.printf("兔子跑了 %d 步…%n", hareStep);
}
}
}
}
//------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
// 練習 Thread 寫龜兔賽跑,拆開來寫成三個檔案:
// Hare.java
public class Hare implements Runnable{
private boolean[] flags = {true,false};
private int totalStep;
private int step;
public Hare(int totalStep){
this.totalStep=totalStep;
}
public void run(){
try{
while(step<totalStep){
Thread.sleep(1000);
boolean isHareSleep = flags[((int)(Math.random()*10))%2];
if(isHareSleep){
System.out.println("兔子睡著了...");
}
else{
step +=2;
System.out.printf("兔子跑了 %d 步…%n", step);
}
}
}catch(InterruptedException ex){
throw new RuntimeException(ex);
}
}
}
//------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
※ 實作 Runnable 介面,好處是有彈性,還有機會繼承其它類別 繼承 Thread 類別,通常是為了直接利用 Thread 類別中的一些方法才會直接繼承 Thread 類別
*/ /******************************************************************************/
/*
執行序有其優先權,可用 Thread 類別底下的 setPriority() 方法設定優先權,可設定值為 1~10,預設是 5 如果超出 1~10 以外的設定值會拋出 IllegalArgnmentException,數字越大優先權愈高,越優先排入;cpu 若相同,則輪流執行。
*/
/*
有幾種狀況會讓執行序進入 Blocked 狀態:
呼叫 Thread.sleep() 方法 進入 synchronized 前競爭物件鎖定的阻斷 呼叫 wait() 的阻斷 等待 input/output 完成 一個進入 Blocked 狀態的執行序可由另一個執行序呼叫該執行序的 interrupt() 方法,讓它離開 Blocked 狀態。
*/
/******************************************************************************/
‧使用 finally
無論 try 區塊中有無發生例外,若撰寫有 finally 區塊,則 finally 區塊一定會執行,如果程式撰寫的流程中先 return 了,而且也有寫 finally 區塊,那 finally 區塊會先執行完後,再將值傳回。
try{
do something…
}catch{
do something…
}finally{ // Always 會執行,且優先過 try-cache
….
}
可以允許的程式寫法:
try-cache
try-finally
try-cache-finally
錯誤的寫法:
catch finally
*/
/****************************************************************************** /
public class FinallyDemo{
public static int test(boolean flag){
try{
if(flag){
return 1;
}
}finally{
System.out.println("finally...");
}
return 0;
}
public static void main(String args[]){
System.out.println(test(true));
}
}
/******************************************************************************
/*/*
java.lang.AutoCloseable 介面
JDK 7 新增了自動關閉資源語法可用的套件,必須實作 java.lang.AutoCloseable 介面,其僅定義了 close() 方法。
package java.lang.*;
public interface AutoCloseable{
void close() throws Exception;
}
*/
/*
執行序流程圖
---
執行序的執行狀態:
起始狀態
Thread t = new Thread();
可執行狀態
Thread t = new Thread();
t.start(); t.yield();
執行狀態
實作 Runnable 介面
繼承 Thread 類別
public void run(){
……
}
非可執行狀態
Thread t - new Thread();
sleep().wait().suspend();
結束狀態
stop()
正常結束
*/
/******************************************************************************/
public class ThreadDemo{
public static void main(String args[]){
System.out.println("Hello Java 測試");
String str = Thread.currentThread().getName();
System.out.println("Thread name: " + str);
System.out.println(Thread.activeCount());
}
}
/******************************************************************************/
// 練習 Thread 寫龜兔賽跑
public class TortoisHareDemo{
public static void main(String args [])throws InterruptedException{
boolean flags[]={true,false};
int totalStep=10;
int tortoiseStep=0;
int hareStep=0;
System.out.println("龜兔賽跑開始…");
while(tortoiseStep < totalStep && hareStep <totalStep){
Thread.sleep(1000);
tortoiseStep++;
System.out.printf("烏龜跑了 %d 步…%n", tortoiseStep);
boolean isHareSleep=flags[((int)(Math.random()*10))%2];
if(isHareSleep){
System.out.println("兔子睡著了…zzz");
}else{
hareStep+=2;
System.out.printf("兔子跑了 %d 步…%n", hareStep);
}
}
}
}
//------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
// 練習 Thread 寫龜兔賽跑,拆開來寫成三個檔案:
// Hare.java
public class Hare implements Runnable{
private boolean[] flags = {true,false};
private int totalStep;
private int step;
public Hare(int totalStep){
this.totalStep=totalStep;
}
public void run(){
try{
while(step<totalStep){
Thread.sleep(1000);
boolean isHareSleep = flags[((int)(Math.random()*10))%2];
if(isHareSleep){
System.out.println("兔子睡著了...");
}
else{
step +=2;
System.out.printf("兔子跑了 %d 步…%n", step);
}
}
}catch(InterruptedException ex){
throw new RuntimeException(ex);
}
}
}
//------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
//TortoiseHareRace.java
public class TortoiseHareRace{
public static void main(String args[]){
Tortoise t = new Tortoise(10);
Hare h = new Hare(10);
Thread tortoiseThread = new Thread(t);
Thread hareThread = new Thread(h);
tortoiseThread.start();
hareThread.start();
}
}
/******************************************************************************/
// 實作 Thread 類別
class HelloThread extends Thread{
HelloThread(String str){
super(str);
}
public void run(){
for(int i=0;i<1000;i++){
String s = Thread.currentThread().getName();
System.out.println(s +" : " + i);
}
}
}
public class TestThread{
public static void main(String args[]){
HelloThread h =new HelloThread("Monic");
h.start();
}
}
/*※ 實作 Runnable 介面,好處是有彈性,還有機會繼承其它類別 繼承 Thread 類別,通常是為了直接利用 Thread 類別中的一些方法才會直接繼承 Thread 類別
*/ /******************************************************************************/
/*
執行序有其優先權,可用 Thread 類別底下的 setPriority() 方法設定優先權,可設定值為 1~10,預設是 5 如果超出 1~10 以外的設定值會拋出 IllegalArgnmentException,數字越大優先權愈高,越優先排入;cpu 若相同,則輪流執行。
*/
// PersonDemo.java
class Person extends Thread{
Person(String str){
super(str);
}
public void run(){
String name=Thread.currentThread().getName();
int priority = Thread.currentThread().getPriority();
Thread.State state = Thread.currentThread().getState();
System.out.println( name + "優先序─ " + priority + ",狀態─ " + state);
for(int i=1;i<=10;i++){
System.out.println(name + "跑完第" + i + "圈");
if(name.equals("Ken") && i%3==0 ){
System.out.println(name + "休息 1 秒…");
}
try{
Thread.sleep(1000);
}catch(InterruptedException ex){
ex.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
public class PersonDemo{
public static void main(String args[]){
Person p1 = new Person("Ron");
Person p2 = new Person("Ken");
p1.start();
p2.start();
System.out.println("正在執行的執行序:" + Thread.activeCount());
}
}
/******************************************************************************//*
有幾種狀況會讓執行序進入 Blocked 狀態:
呼叫 Thread.sleep() 方法 進入 synchronized 前競爭物件鎖定的阻斷 呼叫 wait() 的阻斷 等待 input/output 完成 一個進入 Blocked 狀態的執行序可由另一個執行序呼叫該執行序的 interrupt() 方法,讓它離開 Blocked 狀態。
*/
/******************************************************************************/
// 比較 synchronized 同步
// 無同步
class Company{
static int sum=0;
static void add(int n){
int tmp=sum;
tmp+=n;
try{
Thread.sleep(1000);
}catch(InterruptedException e){}
sum=tmp;
String name=Thread.currentThread().getName();
System.out.println("執行緒:" + name + ",存款為:" + sum);
}
}
class Ccompany extends Thread{
Ccompany(String str){
super(str);
}
public void run(){
for(int i=1;i<=3;i++)
Company.add(100);
}
}
public class SynchronizedDemo1{
public static void main(String args[]){
Ccompany c1 = new Ccompany("Ron");
Ccompany c2 = new Ccompany("Ken");
c1.start();
c2.start();
}
}
/*
輸出結果:

*/
//----------------------------------------------------------------------------
// 加入同步
class Company{
static int sum=0;
synchronized static void add(int n){
int tmp=sum;
tmp+=n;
try{
Thread.sleep(1000);
}catch(InterruptedException e){}
sum=tmp;
String name=Thread.currentThread().getName();
System.out.println("執行緒:" + name + ",存款為:" + sum);
}
}
class Ccompany extends Thread{
Ccompany(String str){
super(str);
}
public void run(){
for(int i=1;i<=3;i++)
Company.add(100);
}
}
public class SynchronizedDemo{
public static void main(String args[]){
Ccompany c1 = new Ccompany("Ron");
Ccompany c2 = new Ccompany("Ken");
c1.start();
c2.start();
}
}
/*
輸出結果:

*/
/******************************************************************************/
//wait
class Company{
static int sale = 0;
synchronized static void add(int n){
String name = Thread.currentThread().getName();
int sum = sale;
sum = sum + n;
System.out.println(name + "銷售量" + n + ",公司銷售量:" + sum);
sale=sum;
}
}
class Ccompany extends Company implements Runnable{
private String id;
public Ccompany(String id){
this.id=id;
}
public void run(){
for(int i=1;i<=10;i++){
Company.add(i);
if(sale > 5){
System.out.println("庫存量超過 5,停止生產…");
try{
wait();
}catch(InterruptedException e){
System.out.println("繼續生產...");
}
}
}
}
}
public class WaitDemo{
public static void main(String args[]){
Thread s1 = new Thread(new Ccompany("S 分店"),"C 分店");
Thread s2 = new Thread(new Ccompany("S2 分店"),"C2 分店");
s1.start();
s2.start();
//s2.interrupt();
}
}
2015年9月6日 星期日
JAVA SL-275_09/06
/*
‧匿名內部類別:簡單的說就是沒有宣告名稱的類別,直接以 {....} 來實作的類別程式碼。
*/
// 利用匿名內部類別來實作 interface
// Anomouse.java
interface Pet{
String attr="aute";
void skill();
void move();
}
public class Anomouse{
public static void main(String args[]){
Pet p = new Pet(){ //無 ;
public void skill(){
System.out.println("拎拖鞋");
}
public void move(){
System.out.println("移動");
}
};
p.skill();
p.move();
}
其中,編譯完後,會出現 Anomouse$1.class 匿名內部類別,其內容包含:
Pet p = new Pet(){ //無 ;
public void skill(){
System.out.println("拎拖鞋");
}
public void move(){
System.out.println("移動");
}
};
若有 n 個內部類別則會以 $流水號 來依序往後排。
/*
靜態內部類別:是在宣告時加上 static ,使其物件實體配置在記憶體 Global 區塊中。
*/
class MyOuter{
static class MyStatic{
public void fooA(){
System.out.println("Hello" + "no static");
}
public static void fooB(){
System.out.println("Hello" + " static method");
}
}
}
public class StaticInnerClass{
public static void main(String args[]){
MyOuter.MyStatic f = new MyOuter.MyStatic();
f.fooB();
f.fooA();
MyOuter.MyStatic.fooB(); //配置為 static 才可以直接執行!
}
}
/***************************************************************************************************/
‧try-catch
‧Bug 的分類:
程式語法上的錯誤。
執行時期的錯誤
ex:陣列元素索引值超出最大範圍 or 整數除以 0
邏輯的錯誤。
try{
// do something…
}catch(Exception e){
// do something…(通常在這做堆疊追蹤)
}
Java 中用依處理錯誤的類別:Throwable, Error, Exception
Error → 指的是系統本身發出的錯誤訊息,也有可能是程式所造成。
Exception → 是一個不正常的程式在執行時期所觸發的事件。
Throwable → 為 Error, Exception 的父類別,若其無法處理,則再往上丟給 JVM 處理。
JVM → Throwable → Error → Exception
try 撰寫時可將容易發生錯誤的程式碼 package 在 try 中。 catch 產生錯誤事件時,catch 進行攔截,並執行此區塊內程式碼。 */ /* ※Exception 大多放在 Input/Ouput 位置,若一開始不知道要放什麼類型的 exception, 則可以先讓程式去 run,看它出現什麼錯誤訊息。 以下為例:
*/
JVM → Throwable → Error → Exception
try 撰寫時可將容易發生錯誤的程式碼 package 在 try 中。 catch 產生錯誤事件時,catch 進行攔截,並執行此區塊內程式碼。 */ /* ※Exception 大多放在 Input/Ouput 位置,若一開始不知道要放什麼類型的 exception, 則可以先讓程式去 run,看它出現什麼錯誤訊息。 以下為例:
public class Test{
public static void main(String args[]){
int arr[] = new int[5];
arr[10] = 7;
System.out.println("end of main method");
}
}
故意讓它 run 出錯誤訊息,再加到 try-catch 中:
Exception in thread "main" java.lang.ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException: 10
at Test.main(Test.java:4))public class Test{
public static void main(String args[]){
try{
int arr[] = new int[5];
arr[10] = 7;
}catch(ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException e){
System.out.println("catch to Exception");
System.out.println("Exception:" + e);
System.out.println("e.Message:" + e.getMessage());
}
System.out.println("end of main method");
}
}
// Average.java
import java.util.*;
public class Average{
public static void main(String args[]){
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
double sum = 0 ;
int count = 0;
int number = 0 ;
System.out.println("Key Integer Num. (exit:0):");
while(true){
try{
number = scanner.nextInt();
if(number == 0 ){
break;
}
sum += number ;
count++;
}catch(InputMismatchException e){
System.out.println("Error:Input is Integer.");
System.out.println("Exception Message:" + e);
break;
}
}
System.out.printf("平均:%.2f%n", sum/count);
}
}
//例外繼承架構:
try{
do something…
}catch(IOException e ){ //直系子類別
e.printStackTrace();
}catch(InterruptedException e){
e.printStackTrace();
}catch(ClassCastException e){ //直系父類別
e.printStackTrace();
}
/*******************************************************************************************/
// Java 7.0 之後 → 多重捕捉 multi-catch
try{
do something…
}catch(IOException | InterruptedException | ClassCastExeption e){
e.printStackTrace(); //堆疊追蹤
}
※左邊的例外不得是右邊的父類別!
/*******************************************************************************************/
/*
‧利用 throw 丟出例外
throw 用來呼叫或傳遞一個例外,所以可以利用它在程式中觸發一個例外。
*/
- throw 例外物件變數 →丟出一個例外物件變數
- throw new Exception(錯誤訊息字串) →丟出一個匿名的例外物件
// FileUtil.java
import java.io.*;
import java.util.*;
public class FileUtil{
public static String readFile(String name)
throws FileNotFoundException{
StringBuilder builder = new StringBuilder();
try{
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(new FileInputStream(name));
String text = null;
while(scanner.hasNext()){
builder.append(scanner.nextLine());
builder.append('\n');
}
}catch(FileNotFoundException ex){
ex.printStackTrace();
throw ex;
}
return builder.toString();
}
}
// Demo.java
import java.io.*;
public class Demo{
public static void main(String args[])
throws Exception{ // 宣告方法中拋出例外
System.out.println(FileUtil.readFile("C:\\java\\0906\\Main.java"));
}
public static void doSome(String arg)
throws FileNotFoundException, EOFException{
try{
if("one".equals(arg)){
throw new FileNotFoundException();
}else{
throw new EOFException();
}
}catch(IOException ex){
ex.printStackTrace();
throw ex; // 執行時拋出例外
}
}
}
//---------------------------------------------------------------------
// 自訂路徑(要同 Demo.java 截取檔案路徑),
隨便編寫內容。 例: C:\java\0906\Main.java
Lccnet
/*******************************************************************************************/
/*
編譯出 .jar 執行檔
*/
A. 以 eclipse 軟體
a. File > New > Java Project > TEST
b. “TEST/src” 右鍵 > New > Class > Main3 (勾選 public static void….)
import javax.swing.*;
public class Main3 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String s = JOptionPane.showInputDialog("Input number");
JOptionPane.showMessageDialog(null, s);
}
}
c. 對 “TEST” 右鍵 > Export > Java > Runnable JAR file
B. 以指令 jar
a. 編寫檔案 Main3.java ,內容同上。
b. 編譯出 Class檔:javac Main3.java
c. jar cfe myJRE.jre Main3 Main3.class
/*******************************************************************************************/
// 堆疊處理
// Main.java
public class Main {
public static String a(){
String text =null;
return text.toUpperCase();
}
public static void b(){
a();
}
public static void c(){
try{
b();
}catch(NullPointerException e){
e.printStackTrace();
Throwable t = e.fillInStackTrace();
throw(NullPointerException) t;
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
try{
c();
}catch(NullPointerException ex){
ex.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
/*******************************************************************************************/
/*
‧ Assert 斷言
assert boolean_expression;
assert boolean_expression:detail_expression;
boolean_expression 若為 true 則什麼事都不會發生;
若為 false 則會發生 java.lang.AssertionError;
*/
//----------------------------------------------------------------------------
// AssertDemo.java
public class AssertDemo{
final int ACTION_STOP=0;
final int ACTION_RIGHT=1;
final int ACTION_LEFT=2;
final int ACTION_UP=3;
public static void main(String args[]){
new AssertDemo().play(0);
new AssertDemo().play(1);
new AssertDemo().play(2);
new AssertDemo().play(3);
// new AssertDemo().play(5);
new AssertDemo().testScore(0);
new AssertDemo().testScore(100);
new AssertDemo().testScore(-1);
}
public void testScore(int score){
assert(score >= 0 && score <= 100):"成績錯誤";
System.out.println("score = " + score);
assert(score >= 0 && score <= 100):"成績錯誤";
System.out.println("score = " + score);
}
public void play(int action){
switch(action){
case ACTION_STOP:
System.out.println("停止撥放");
break;
case ACTION_RIGHT:
System.out.println("向右撥放");
break;
case ACTION_LEFT:
System.out.println("向左撥放");
break;
case ACTION_UP:
System.out.println("向上撥放");
break;
default:
assert false : "非定義的常數";
}
}
}
/*
※注意,編譯完執行要加 -ea 參數啟用Assertionjavac AssertDemo.java
java -ea AssertDemo
*/
/*******************************************************************************************/
訂閱:
意見 (Atom)